Hand tendons help us text, play instruments, and hold a cup of coffee without even thinking. The shocker? These tiny connectors are so strong that hand tendons can transmit forces up to ten times your body weight during intense activity. Most people worry about bone breaks or muscle pulls, but it is often tendon injuries that leave even the healthiest hands stiff or weak. Understanding how hand tendons actually work and what happens when they break might change everything you thought you knew about your grip.
Table of Contents
- What Are Hand Tendons And Their Functions?
- Why Is Hand Tendon Repair Important?
- How Hand Tendon Repair Works: Key Principles
- Recovery Process And Rehabilitation After Surgery
Quick Summary
| Takeaway | Explanation |
| Hand tendons connect muscles and bones. | They transform muscle contractions into precise movements, facilitating complex hand actions like gripping and lifting. |
| Timely tendon repair is crucial for recovery. | Delayed treatment can result in permanent stiffness, reduced strength, and chronic pain, affecting daily life. |
| Surgical techniques restore tendon functionality. | Methods like tendon suturing and grafting help reconnect damaged tendons, ensuring optimal recovery. |
| Rehabilitation is essential post-surgery. | A structured recovery approach, including various motion phases, is vital for restoring strength and mobility. |
| Patient commitment enhances rehabilitation success. | Active participation in therapy and adherence to movement restrictions can significantly improve healing outcomes. |
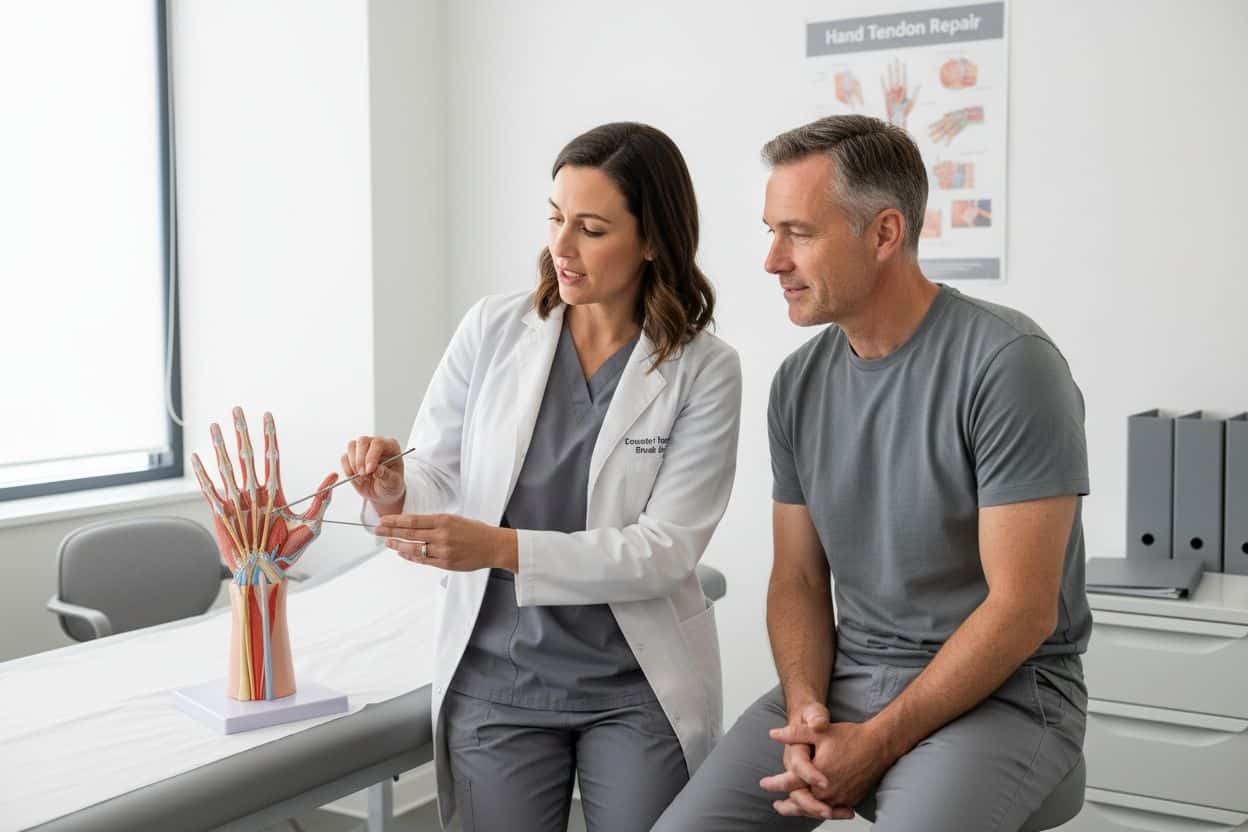
What Are Hand Tendons and Their Functions?
Hand tendons are critical biological connectors that enable complex hand movements and provide structural integrity to our upper extremity functionality. Orthopedic research reveals these robust, fibrous tissues link muscles to bones, transforming muscular contractions into precise mechanical movements.
Anatomical Structure and Composition
Tendons are dense, tough connective tissues composed primarily of collagen. Unlike muscles, they do not contract themselves but instead transmit the force generated by muscle contractions directly to bones. In the hand, two primary tendon groups exist:
- Flexor Tendons: Located on the palm side, these enable finger bending and gripping actions
- Extensor Tendons: Positioned on the back of the hand, these facilitate finger straightening and opening movements
Functional Mechanics of Hand Tendons
The intricate mechanism of hand tendons allows for remarkable dexterity. When muscles contract in the forearm, tendons pull the corresponding bones in the fingers, creating precise movements. This complex system enables everything from delicate tasks like threading a needle to powerful actions like lifting heavy objects.
If you want to learn more about advanced hand surgical techniques related to tendon management, read our guide on tendon transfer procedures.
Understanding hand tendon functions provides crucial insight into how our hands perform sophisticated movements, highlighting the incredible engineering of human musculoskeletal anatomy.
Why Is Hand Tendon Repair Important?
Hand tendon repair is a critical medical intervention that prevents long-term functional disability and restores essential hand mobility. Surgical research emphasizes the urgent need for timely repair to maintain optimal hand performance and prevent permanent complications.
Consequences of Untreated Tendon Damage
Ignoring tendon injuries can lead to devastating consequences for hand functionality. Without proper repair, patients may experience:

- Permanent Stiffness: Unrepaired tendons can cause joints to become rigid and immobile
- Reduced Grip Strength: Damaged tendons significantly compromise hand strength and dexterity
- Chronic Pain: Unresolved tendon injuries often result in persistent discomfort
Restoring Functionality and Quality of Life
Proper hand tendon repair goes beyond physical restoration. It directly impacts an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, work responsibilities, and maintain independence.
Surgical interventions can help patients regain:
- Full range of motion
- Precise motor control
- Painless hand movements
If you are interested in understanding more advanced surgical approaches, explore our comprehensive guide on hand surgical techniques.
Ultimately, hand tendon repair is not just a medical procedure but a pathway to reclaiming personal autonomy and maintaining quality of life.
How Hand Tendon Repair Works: Key Principles
Hand tendon repair is a sophisticated surgical procedure that requires precision, advanced techniques, and comprehensive understanding of hand biomechanics. Medical research highlights the complex nature of reconnecting and restoring damaged tendon structures to ensure optimal functional recovery.
Surgical Reconstruction Techniques
Surgeons employ multiple advanced approaches to repair damaged hand tendons, focusing on restoring smooth movement and structural integrity. The primary reconstruction techniques include:
- Direct Tendon Suturing: Precisely reconnecting severed tendon ends using specialized microsurgical techniques
- Tendon Grafting: Replacing severely damaged tendon sections with healthy tissue from other body regions
- Tendon Transfer: Repositioning functional tendons to restore lost movement capabilities
Biomechanical Healing and Recovery Principles
Successful tendon repair involves more than surgical intervention. The healing process requires careful management to prevent complications and ensure proper tissue regeneration. Critical factors include:
- Maintaining appropriate tension during suturing
- Protecting the repair site during initial healing stages
- Implementing strategic rehabilitation protocols
If you want deeper insights into advanced hand surgical approaches, explore our comprehensive surgical techniques guide.
Ultimately, hand tendon repair represents a delicate balance between surgical skill, biological understanding, and patient-specific rehabilitation strategies.
The table below summarizes the four key surgical reconstruction techniques discussed, outlining the method and primary purpose of each approach.
| Technique | Method | Primary Purpose |
| Direct Tendon Suturing | Reconnecting severed tendon ends with specialized sutures | Restore continuity and strength |
| Tendon Grafting | Replacing damaged tendon segments with healthy tissue | Repair areas with tissue loss or irreparable damage |
| Tendon Transfer | Relocating functional tendons to new insertion points | Restore movement when original tendons are not repairable |
Recovery Process and Rehabilitation After Surgery
Hand tendon repair rehabilitation is a carefully structured journey designed to restore hand functionality and prevent potential complications. Medical studies demonstrate that comprehensive rehabilitation is crucial for achieving optimal surgical outcomes and long-term hand performance.
Staged Rehabilitation Approach
Recovery from hand tendon repair is not a linear process but a strategic, multi-phase approach that adapts to the patient’s healing progression. The rehabilitation stages typically include:
- Protection Phase: Immobilizing the hand to allow initial tissue healing
- Passive Motion Phase: Gentle, controlled movements initiated by a therapist
- Active Motion Phase: Patient-driven exercises to rebuild strength and flexibility
- Functional Restoration Phase: Returning to normal daily activities and work tasks
Critical Rehabilitation Considerations
Successful rehabilitation demands patient commitment and professional guidance. Key elements that influence recovery include:
- Strict adherence to prescribed movement restrictions
- Consistent participation in physical therapy sessions
- Patience with the healing process
- Proper pain and inflammation management
Learn more about our comprehensive joint recovery strategies.
Ultimately, hand tendon repair rehabilitation is a collaborative process between the patient, surgeon, and rehabilitation specialists, focused on restoring maximum hand function and quality of life.
This table outlines the four main phases of hand tendon repair rehabilitation, highlighting the purpose and activities involved in each stage to clarify the recovery process for patients.
| Rehabilitation Phase | Purpose | Typical Activities |
| Protection Phase | Allow initial tissue healing | Hand immobilization (splint/cast) |
| Passive Motion Phase | Begin safe movement, prevent adhesions | Therapist-guided gentle movements |
| Active Motion Phase | Rebuild strength and flexibility | Patient-initiated, controlled exercises |
| Functional Restoration Phase | Regain normal function and daily use | Practice daily living and work tasks |

Get Expert Relief for Hand Tendon Injuries in Austin
Are you struggling with pain, stiffness, or weakness after a hand tendon injury? Regaining hand movement and strength is not just about surgery but about trusting a specialist who understands the delicate structure and critical function of hand tendons. If you have learned from this article how untreated tendon damage can lead to permanent limitations and ongoing discomfort, it is time to explore advanced orthopedic care designed for your unique needs. Discover how our patient-centered approach at Austin Hand To Shoulder delivers real results for those dealing with tendon repairs and complex upper limb injuries.
Experience the difference of care from a fellowship-trained, board-certified surgeon. Schedule your first visit or get more information about treatment options through our orthopedic recovery resources. Every day you wait puts your recovery and quality of life on hold. Regain your hand function and confidence with Austin Hand To Shoulder and start your healing journey today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is hand tendon repair, and why is it necessary?
Hand tendon repair is a surgical procedure that reconnects damaged tendons in the hand to restore movement and functionality. It is necessary to prevent long-term disability and ensure you can perform daily activities like gripping or typing.
How long does recovery from hand tendon repair take?
Recovery from hand tendon repair typically spans several weeks, with full function potentially returning within 3-6 months. Follow your surgeon’s post-operative guidelines closely to ensure a successful healing process.
What does the rehabilitation process involve after hand tendon repair?
The rehabilitation process includes multiple stages, starting with immobilization, followed by passive and then active motion exercises. Adhere to your physical therapist’s instructions to maximize your hand’s recovery and strength restoration.
What are some common complications to watch for after hand tendon repair?
Common complications include stiffness, reduced grip strength, and chronic pain if the repair isn’t monitored properly. Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately to address potential issues promptly.
How can I prepare for my hand tendon repair surgery?
Preparing for hand tendon repair surgery involves discussing your medical history, understanding the procedure, and arranging for post-surgery assistance. Take time to clarify any questions you have during your pre-operative consultation to ensure you are well informed.
What should I expect in terms of pain management after the procedure?
Pain management after hand tendon repair typically involves prescribed medications and at-home care strategies. Follow your healthcare provider’s pain management plan closely to maintain comfort and promote healing.